oh-my-docs
Summary for developers
Project maintained by italkso Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
Swift 编程
1.Swift 简介
Swift 的现代编程特性
-
变量使用前先初始化
-
检查数组索引是否越界,检查整数溢出
-
使用可选类型(Optional)显式处理 nil 值
-
自动内存管理(ARC)
-
允许从未知错误中恢复
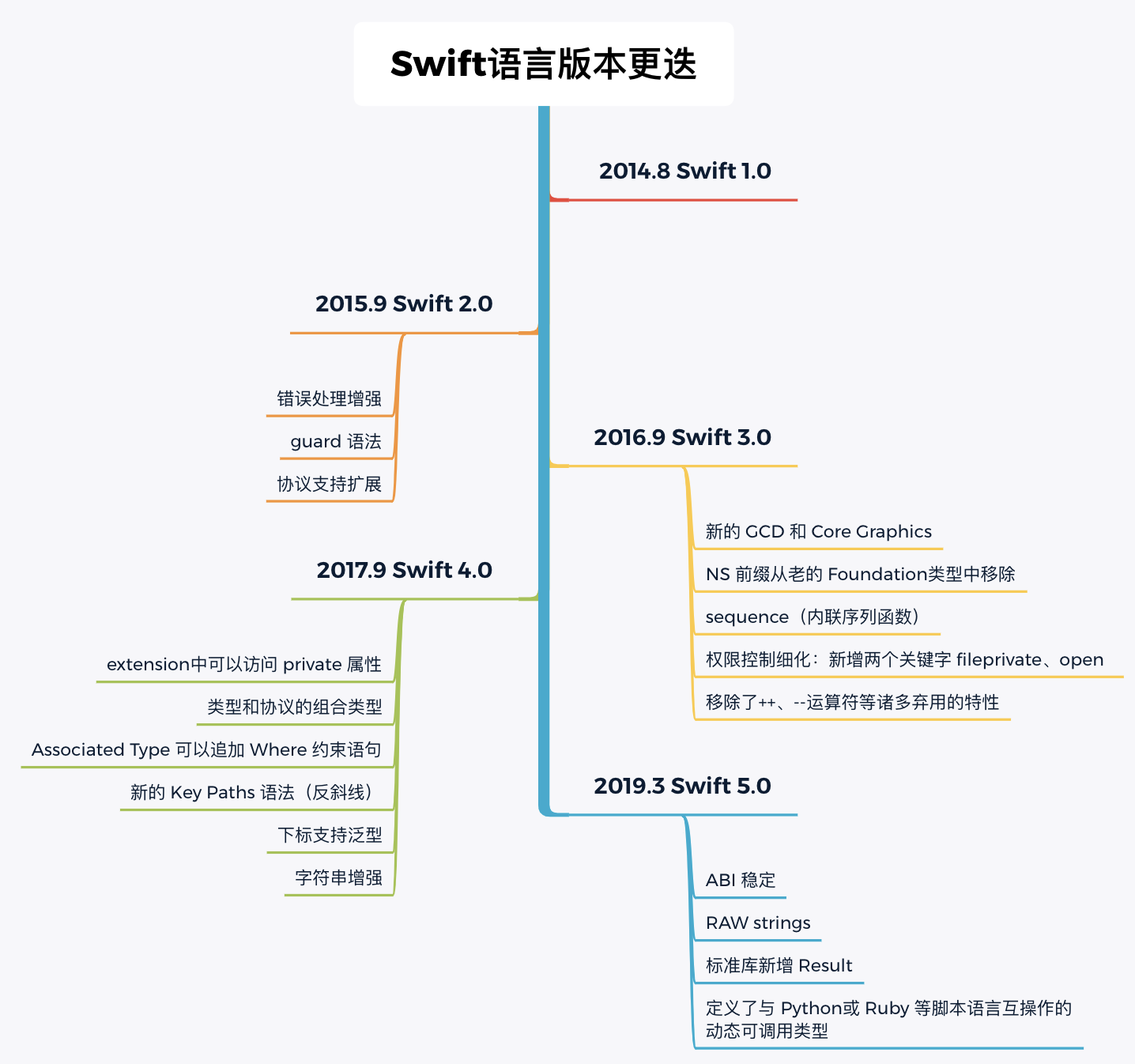
Swift 的版本更迭
Swift的特点
-
编程范式
Swift 支持「面向协议编程」、「函数式编程」、「面向对象编程」。Objective-C 仅支持面向对象编程。
-
类型安全
Swift 是类型安全的,而 Objective-C 是非类型安全的。
-
值类型增强
struct、enum、tuple、基本数据类型(用 struct 实现)都是值类型,值类型具有不变性,独立性、可交换性等特点。而 Objective-C 中的 NSNumber、NSString 、集合类对象都是指针类型。
-
枚举增强
Swift 中的枚举可以使用整型、浮点型、字符串型,可以拥有属性和方法,支持泛型、协议和扩展等。而 Objective-C中的枚举仅仅是一个标记值。
-
泛型支持
Swift 支持泛型和泛型的类型约束,而 Objective-C 对泛型约束的支持仅仅停留在编译器警告阶段。
-
协议和扩展
Swift 对协议的支持很丰富,可配合扩展、泛型、关联类型实现面向协议编程,还可用于值类型。而 Objective-C 的协议缺乏强约束。
-
函数和闭包是 first class
Swift 中的函数和闭包一等公民,你可以直接定义函数类型变量,可以将函数和闭包作为其他函数参数传递,也可以把函数和闭包作为函数的返回值返回。而 Objective-C 中的函数时二等公民,为了模拟 swift 中类似的效果,需要selector 封装或者使用 block。
2. 语法要点
此处总结了使用 Swift 编写代码的一些要点,如果需要更详细的说明,后文相关章节会有展开。
使用 Xcode、 Playground、swiftc 或 REPL 都可以编译和运行 Swift 代码。
使用 Xcode 的 Playground 文件练习 Swift 语法时,请记得在Xcode 的 Playground文件中使用import Foundation导入 Swift 语言及核心功能框架。长按并选择底部的「Automatically Run」,Playground 就会在在用户每次新增代码后,自动运行并给出代码执行结果。
注释和打印
单行注释用//,多行注释用/* */。print()函数默认添加了换行\n,如果不想要换行,使用 print()给 terminator 赋值一个期望的分隔符。
public func print(_ items: Any..., separator: String = " ", terminator: String = "\n")
代码规范
包括大小写、空行、命名、标点符号等。
-
代码换行时使用键盘 Return 按钮。
-
花括号中代码前需空格时,使用 Tab 键按钮。
-
Swift 语言自带的关键字、自定义函数、常量名和变量名均遵循驼峰命名法。
-
使用英文标点符号。
常量和变量
let 和 var
- 使用
let声明常量,初始化后无法修改内容;使用var声明变量 ,初始化后可以随意修改内容。 - 使用赋值号
=将其右侧的内容赋给左侧的变量,assign 即是赋值,第一次赋值叫做初始化(Initialize)。 - 常 / 变量仅能在其作用域(Scope)内被使用,作用域一般是该变量的声明所处的花括号中。
命名规则(见名知义)
-
一般使用「驼峰命名法」
-
常量名和变量名可以包含大部分字符(包含 Unicode字符)
-
常量名或变量名必须唯一
-
存储值时必须保证值的类型与常量或变量的类型相匹配。
命名禁忌
- 不能含有空格、数学符号、箭头、专用的 Unicode标量值、线条或框形图字符等
- 不能以数字开头
- 应当避免使用 Swift 的关键字作为常量名或变量名
运算符
一元(unary)运算符只需要一个操作数,前缀(-a、!b)、后缀(可选类型的?和!)均可。 二元(binary)运算符需要两个数,中缀( 3 + 4 )。条件运算符(?: )是唯一的三元(ternary)运算符。
-
算术
+ - * / %,默认情况下Swift 的算术运算符不允许值溢出,以避免存储越界时出现意外结果。Swift 中的整数除法所得结果是直接向下取整,一元加减即是正负号。
a % b是取余( remainder)运算符。在 Swift 中,对负数使用运算符%是求余数而不是模。a % b与a % -b结果相同。 -
赋值
使用
=初始化或给变量重新赋值,使用+= -= *= /=等一次性完成运算并赋值,即复合赋值。为了避免开发者误将赋值运算符用作恒等运算符(==),赋值本身不返回值。
-
逻辑
&& || !,常用在条件判断语句中,注意&&和||左结合。 -
比较
== != > >= < <=,返回一个布尔(Bool)值,是条件判断语句中常用的运算符。 -
区间
a…b、a..<b、a…或…b,常与循环语句搭配使用。a..<b在数组等从 0 开始的数据结构中特别有用。 -
三元条件运算符
x ? a : b,平衡代码的简洁性和易读性,不提倡过度使用。 -
Optional 相关
?- 定义可选类型!- 强制解包??- 合并空值a ?? b为可选类型提供默认值,即有值时将a解包,没有值时返回预先指定的默认值b。 -
Type casting
is是类型检查运算符。as?向下类型转换的条件形式(the conditional form of downcast ),不确定是否会成功时用。as!向下类型转换的强制形式(the forced form of downcast ),确定总会成功时用。 -
===和!==判断运算符两边的指针是否相同,即判定两个 instance 是不是同一个。
-
圆括号(Parentheses)
在不需要圆括号时使用圆括号,可以提高复杂表达式的可读性。
// 门禁访问示例 if (enteredDoorCode && passedRetinaScan) || hasDoorKey || knowsOverridePassword { print("Welcome!") } else { print("ACCESS DENIED") } // 打印 "Welcome!"
控制流
-
条件判断(Condition)
if else、else if、?:、switch、default -
循环(Loop)
for-in:可用于集合类型及区间while:while condition {},优先判断是否满足条件repeat-while:repeat {} while condition,运行完第一遍代码后才进行条件判断
类型
因为存储空间总是有限的,计算机所作的计算也只是近似计算,所有需要类型这个概念。
按照存储性质类型划分,可以分为值类型与引用类型。基本类型是指编程语言直接提供的类型,而enum、class、struct等是自定义类型。
Swift 是强类型语言 (strongly typed language),要么直接完成初始化,Swift 会根据内容推断常量或变量的类型,即类型推断(Type Inference);要么明确明确标出常量或变量的类型,即类型注解(Type Annotations)。按下 Option 键并点击任意常/变量,Xcode 就会显示其类型。
使用String(42)将 Int 42 转换为 String呢,就叫做类型转换(Type Casting)。
你还可以适度使用typealias关键字给基础类型或者更复杂的类型起一个类型别名,比如typealias name = String。
常用的类型
-
基本类型
最基本的数据类型,
Int、Double、Bool、String,值类型。字符串插值
\(),字符串拼接+。 -
集合类型
处理批量数据,数组
[], 字典[:], Set[Set],值类型。 -
元组
将多个值作为一个单一的复合值返回,
()。 -
函数和闭包
func,{},提供功能, 引用类型。 -
可选类型
显示处理空值(实际属于枚举类型),
Optional?,值类型。 -
结构 struct
创建自定义类型,值类型。
-
枚举 enum
存储有限类别的事务,允许创建新类型,关键字
enum…case,值类型。 -
类 class
创建自定义类型,引用类型。
值类型和引用类型
硬盘容量大,可以永久存储( Permanent Storage)信息。而内存空间有限,仅被用来临时存放(Temporary Storage)正在运行的应用。
Int、Double、Bool、Enum、Struct、Array、Dictionary等都是值类型(Value Type),它们直接将信息存储在内存的存储单元中,这些类型的常量或变量所指代的就是内存中的信息本身。
Class是属于引用类型(Reference Type),引用类型的变量存储的是内存中值所对应的内存地址,即指针(Pointer)。
集合类型
-
Array
语法
[Type],[[Type]],逻辑上的多维数组在内存中仍表现为一维数组。数组 Array 适合存储大量不确定的数据。
属性
count,min,isEmpty,contains(_:)方法
增 -
append(_:)或+=,insert(_:at:)删 -
remove(at:),removeLast(),removeAll(),removeSubrange(2...5)查 -
arrayName[index],randomElement(),firstIndex(of:)改 -
arrayName[index] = newValue,sort(),shuffle()原位修改,map()使用尾随闭包语法返回新数组,filter()使用尾随闭包语法返回符合筛选条件的新数组。 -
Dictionary
语法
[key:value],可以将字典与数组混合使用,把字典作为数组的元素。属性
count,isEmpty,contains(where:)方法
增 -
dictionaryName[key] = value删 -
dictionaryName[key] = nil改 -
dictionaryName[key] = newValue查 -
dictionaryName[key] -
Set
略。
元组
Tuple
可选类型
-
可选类型(Optional)是一个枚举类型 (enum)
Optional.none表示nil,Optional.some表示包裹值。 -
声明和强制解包
在现有类型后方加
?可以声明一个可选变量,使用!强制解包(Force Unwrap) -
可选绑定
可选绑定(Optional Binding)是指先判断,有值就赋给常量或变量。
if let语法:所创建的常量仅能在花括号 {} 内被使用。guard let语法:所创建的常量可以在guard let自身的花括号外使用。 -
可选链
使用可选链(Optional Chaining) 为可选类型增加默认值 ,语法为
??。
结构、枚举、类、扩展和协议
-
使用 结构(struct)自定义新类型
-
使用 枚举(enum) 自定义新类型,将有限种类的数据归类
-
使用 类(class) 自定义新类型,将数据通过层级关系归类
-
使用 扩展 (extension)向现有的任意类型添加新内容
-
使用 协议(protocol)
权限控制 Access Control
权限控制( Access Control)分为 5 个级别,即open、fileprivate、internal、private、public。
异常处理
Swift 使用 Error 协议处理应用中的异常 ,你可以使用do-try-catch、 try? 或 try!处理可能的异常。
3. 函数和闭包
函数和闭包都是引用类型,当你把一个函数或闭包赋给一个常量或变量时,实际上是在引用函数和闭包。
函数(Function)
函数是 first-class 类型,可以将函数类型作为参数传递和返回值返回。
// Define a function
func functionName(argumentLabel parameter: ParameterType) -> ReturnType {
// Implementation
return ReturnType()
}
// Call a function
functionName(argumentLabel: actualValue)
-
完整的函数定义
包括关键字
func,函数名,参数列表(),返回值和实现函数功能的代码。 -
parameter是外来数据
函数可以使用 parameter 引入外来数据来执行其自身功能。parameter List 为空则表明函数不需要任何外来数据。
-
argument 是使用函数时的具体数值
通过函数名和参数列表可以调用函数。这时,应明确给出该函数中每一个参数的具体数值 。
-
标签及默认值
使用 Argument Label 是为了提高函数调用时参数的可读性。标签名(如
to)不一定要与参数名(如name)相同,在调用时也可以使用_省略标签名。 -
返回值
Return Value 指函数所返回的结果,Return Type是指返回值的类型。当代码中仅包含一个可以返回的数值时,可以省略 return 关键字。
-
函数重载
Function Overload 指函数名相同,但其它方面不同的函数。
-
最佳实践
应将待解决的问题划分成多个小函数,而不是把所有功能放入一个函数。
根据函数使用情况来回推函数定义,先思考函数的功能,然后考虑要处理的参数以及是否需要返回值。
示例:
func greeting() {
print("Hello")
}
func greeting(to name:String) {
print("Hello,\(name)")
}
greeting()
greeting(to: "Jobs")
闭包(Closure)
-
Closure Expression
闭包省略了函数名,并将花括号前移,同时增加了
in语法。通常将闭包作为函数的参数使用。
// Closure Expression
{(parameters) -> ReturnType in
statements
}
let chars = ["a", "e", "i", "o", "u"]
var reversedChars = chars.sorted(by: { (s1: String, s2: String) -> Bool in
return s1 > s2
})
reversedChars = chars.sorted(by:{s1, s2 in return s1 > s2})
reversedChars = chars.sorted(by:{s1, s2 in s1 > s2})
reversedChars = chars.sorted(by:{ $0 > $1})
reversedChars = chars.sorted(by:>)
- Trailing Closures
let chars = ["a", "e", "i", "o", "u"]
var reversedChars = chars.sorted { (s1: String, s2: String) -> Bool in
return s1 > s2
}
reversedChars = chars.sorted {s1, s2 in return s1 > s2}
reversedChars = chars.sorted {s1, s2 in s1 > s2}
reversedChars = chars.sorted { $0 > $1}
4. 结构、类和 OOP
面向对象编程OOP
面向对象编程(Object-oriented programming,OOP)就是「整理归类」,即将待用物品归类,并根据类别赋予不同的功能和属性。OOP 的实质是间接(indirection)技术。
抽象(Abstraction)、封装 (Encapsulation)、继承 (Inheritance)、多态 (Polymorphism)是OOP 的四个重要属性。
Swift 中,类 class 与结构 struct 都用来创建自定义类型,都具有「属性、初始化器、方法」。关键字不同只是两者在语法上的区别。有兴趣可以参考 CS193P 课程中关于结构和类的比较。
struct 和 class 的核心差异是:
-
struct 是值类型,而 class 是引用类型
在存储逻辑上的差异。
-
struct 只支持一个层级,class 支持创建多个层级的父子关系
class 支持继承。
-
struct 自带默认的初始化器,而 class 必须写明初始化器
如果你不提供初始化器,编译会报错,错误信息类似
Class 'MyClass' has no initializers。
对于 Apple 官方框架来说,适用于反复使用的框架一般定义为 class,以减少重复占用过多内存。而不需要继承、不适合反复使用的实体常被定义为 struct。Apple 官方文档建议,当创建新的自定义类别时,首先定义为 struct。只有你需要用到 class 继承的特性,或者是作为引用类型的特性时,再将关键字更换为 class。
结构
struct 用来定义新的类型,是 Swift 语言的核心组成部分。一个常见的 struct 可能包含属性、初始化器和方法。用属性来处理数值、用方法来书写功能。Swift 中的Int、 Double、Array、Dictionary 等数据类型实际上都是struct 。
struct StructName {
// Instance or Type Property, Stored or Computed Property, Lazy Property
var property: Int
// Default Initializer, Custome Initializer
init(property: Int) {
self.property = property
}
// Instance or Type Method, Mutating Method
func someMethod() {
//
}
}
参考示例:
lazy 表示把赋值操作 currentHealth = maxHealth 延迟到 currentHealth 真正需要被使用时。
// MARK: - Structure
struct Player {
// MARK: - Property
static var allPlayers: [Player] = [] // Type Property
var name: String
var livesRemaining = 5 {//Property Observer
willSet {
print("Warning: \(livesRemaining) Lives")
}
didSet {
if livesRemaining != 0 {
print("I'm Back!")
} else {
print("Game Over.")
}
}
}// Property Observer
let maxHealth = 100
lazy var currentHealth = maxHealth
var isPlayerOutOfLives: Bool {
get {
livesRemaining == 0 ? true : false
}
set {
if newValue {
livesRemaining = 0
}
}
}// Computed Property
// MARK: - Initializer
init(name: String) {
self.name = name
}// Default initializer with a default value
init(name: String, livesRemaining: Int, currentHealth: Int) {
self.name = name
self.livesRemaining = livesRemaining
self.currentHealth = currentHealth
}// Default initializer without a default value
init(name:String, livesRemaining: Int) {
self.name = "VIP" + name
self.livesRemaining = livesRemaining
currentHealth = 10000
}// Customer initializer
// MARK: - Method
func welcomePlayer() {
print("Current Player: \(name)")
}
mutating func damaged(by health: Int) {
currentHealth -= health
if currentHealth <= 0 && livesRemaining > 0 {
livesRemaining -= 1
currentHealth = maxHealth
}
if livesRemaining == 0 {
print("Game Over")
}
}
mutating func stateReport() {
print("Current Health\(currentHealth),\(livesRemaining)Lives Left")
}
static func recentAddedPlayer() -> Player {
allPlayers[allPlayers.count - 1]
}// Type Method
}
var playerX = Player(name: "X")
var playerY = Player(name: "Y", livesRemaining: 10, currentHealth: 100)
Player.allPlayers.append(contentsOf: [playerX, playerY])
print("Player Added Recently: \(Player.recentAddedPlayer().name)")
playerX.stateReport()
playerX.isPlayerOutOfLives = true
playerX.damaged(by: 50)
playerX.stateReport()
playerX.damaged(by: 30)
playerX.stateReport()
-
值类型和引用类型
结构(struct)和枚举(enum)是值类型,而类(class)、函数和闭包是引用类型。
-
创建 Instance
使用语法「
名称(属性的值)」创建结构、枚举和类的 Instance 。 -
点语法
使用点语法调用 Instance 的属性及方法。
-
Type Property/Method
添加关键词 static 的属性及方法分别叫做类型属性(Type Property)和类型方法(Type Method),代表其内容与结构相关。
当需要将结构作为一个独特的类型来提供数据时,就要用到类型属性。
定义类型属性:
static var allPlayers: [Player] = []。调用类型属性:
结构名.类型属性,如Player.allPlayers.append(contentsOf: [playerWang, playerZhou])。类型方法。
-
Instance Property/Method
未添加关键词 static 的属性及方法分别叫做Instance Property和Instance Method,代表其内容仅能用于 instance 中,如调用Instance 方法
playerWang.stateReport()。
// Definition of Structure
struct Resolution {
var width = 0
var height = 0
func printInfo(){
print("Width:\(width),Height:\(height)")
}
}
// Create an instance and initialize members of structure Resolution
let someResolution = Resolution(width: 640, height: 480)
print("\(someResolution.height)")
someResolution.printInfo()
属性
-
属性
在结构和类中定义的常量或变量叫做属性(Property)。
-
lazy
使用关键词可以告知编译器先忽略 lazy 关键词后的赋值语句。
-
属性观察器
属性观察器(Property Observer)负责监视属性的变化,并在属性的值发生变化时作出反馈。触发时机:
willSet:检测到该属性将要发生变化,新的值为newValue。didSet:已将新的值赋给该属性,被更改的值为oldValue。 -
计算属性
计算属性 (Computed Property)是指本身不存储任何数值,通过计算现有属性获得结果的属性。关键词为
get和set。
方法
-
方法
定义在结构、枚举和类中的函数叫做方法(Method) 。
-
mutating
当方法需要更改属性的值时,需要在方法的关键词 func 前加上关键词 mutating。
初始化器
初始化器(Initializers)是特殊的方法,用于给 struct 创建 instance ,使用初始化器是为了确保 Instance 中的所有属性都被赋值。Swift 允许开发者自定义初始化器。
通常使初始化器的参数与结构的属性同名,可以使用 self 关键词区分,关键词 self 等同于当前的instance。
一般Swift 会自动提供两个初始化器的版本,一种将默认值考虑进去,只需开发者提供剩余参数即可,如 init(name: String);另一种不考虑默认值,要求提供所有参数,如 init(name: String, livesRemaining: Int, currentHealth: Int)。
类
使用类(Class)可以实现上述 OOP 的四个属性。
继承
A class ( subclass ) can inherit methods, properties, and other characteristics from another class ( superclass ).
class SomeBaseClass {
// Definition of base class
}
class SomeSubclass: SomeSuperclass {
// Definition of subclass
}
- 继承使用冒号语法,即
SubClass: SuperClass。 - 如果向子类添加的内容已在父类中存在,使用关键字 **override **,表示以子类覆盖后的内容为准。
- 使用关键字 super 可以直接调用父类实体,如
super.init()。你也可以在子类中完整地写出对初始化器中所有变量的赋值,但这样比较麻烦。
多态
- 处理多种子类是OOP 中多态的体现
5. 可选类型和枚举
// Enumerations
enum CompassPoint {
case north, south, east, west
mutating func turnNorth() {
self = .north
}
}
var currentDirection = CompassPoint.west
let rememberedDirection = currentDirection
currentDirection.turnNorth()
print("The current direction is \(currentDirection)")
print("The remembered direction is \(rememberedDirection)")
数组( Array) 适合存储大量不确定的数据,枚举(Emuration) 适合存储有限类别的事务,使用枚举可以创建一个新类型。枚举的关键词是 enum...case。使用枚举的方式是「枚举名称.枚举中的种类」。
可选类型(Optional)实际上就是一个包含两个状态的枚举,Optional.some存储数值,Optional.none存储空值。你可以给 policyNote 赋值 nil,或直接根据其枚举的属性给它赋值为 Optional.none,其结果完全一致,如下图所示。。
除了单独使用外,你也可以将枚举与 switch 语句搭配使用,用于对枚举中不同类型的事务做区别处理。
6. 协议
协议
A protocol defines a blueprint of methods, properties, and other requirements that suit a particular task or piece of functionality. The protocol can then be adopted by a class, structure, or enumeration to provide an actual implementation of those requirements.
protocol MyProtocol {
var name: String { get }
init(name:String)
}
struct FirstStruct: MyProtocol {
var name: String
init(name:String) {
self.name = name
}// You can omit these codes in structure because of its default initializer
}
struct SecondStruct {
var name: String
}
extension SecondStruct: MyProtocol {
// Some Code
}
class ClassName: SuperClass, MyProtocol {
// Defination of Class
// Implementation of ProtocolName
}
协议是规则,遵守协议的结构、类或枚举需要实现协议规定的功能。遵守协议可以写在 结构、类或枚举中,也可以用扩展来写。
面向协议编程(Protocol Oriented Programming,POP)是为了代码复用,即整理项目中的 struct、class、enum等代码,提取逻辑层面的内容后将这些能够复用的部分写出协议。因此,protocol 中的属性、方法及初始化器都有其特殊之处。
-
protocol 中的属性关键词
var,只读{ get }表示属性的值允许被 instance 读取, 可读可写`{ get set }属性的值可以被实体 instance 读取或变更。 -
protocol 中的初始化器及方法不包含具体实现。
常见的协议类型
Equatable 协议和 Comparable 协议用于比较、Hashable 协议和 Identifiable 协议用于识别、Codable 协议用于存取。
-
Equatable
Equatable 协议 用于判断两个「自定义类型」的Instance 的值是否相等(comparasion for value equality)。所有基础类型( String、Double、Int、Array 等)都默认遵守 Equatable 协议。
当自定义类型中不只基础类型时,需要写上类方法
static func == (Self, Self) -> Bool,因为这是实现Equatable 协议要求必须(Required)提供的。 -
Comparable
Comparable 协议 用于判断先后问题,遵守了该协议的类型可以使用关系运算符进行比较。
-
Hashable
哈希 (Hash) 是指将现有的数据结构通过一定的运算转化为一个随机的、不可重复的、独特的值,这个值就叫哈希值,是一个整数。Swift 提供了哈希值运算,开发者通过添加
: Hashable只需要遵守 Hashable 协议即可。Hashable 协议继承自 Equatable 协议。结构 struct 的所有存储属性(stored properties)和枚举 enum 的所有关联值(associated values)都必须遵守 Hashable 协议。
-
Identifiable
Identifiable 协议 要求遵守该协议的必须添加一个名为 id 的属性,该属性必须包含一个可哈希的数值,名为 id。Swift 提供的
UUID()函数可以用来生成唯一的 ID ,用法是var id = UUID()。Identifiable 协议还是许多 SwiftUI 视图背后的前置数据条件,SwiftUI 会根据这个独特的 id 来判断视图的复用。
-
Codable
Codable 协议 的声明如下,Codable 是 Encodable 和 Decodable 协议的类型别名,遵守Codable 协议的数据支持存取。编码 (Encode)就是将内存中临时存储的信息转化成硬盘里永久存储的信息,解码( Decode)则是将硬盘里的信息读入内存。
typealias Codable = Decodable & Encodable
7. 扩展
Extensions add new functionality to an existing class, structure, enumeration, or protocol type.
// Extension Syntax
extension SomeType {
// New functionality
}
// Extend an existing type to make it adopt one or more protocols
extension SomeType: SomeProtocol, AnotherProtocol {
// Implementation of protocol requirements
}
// Computed Properties
extension Double {
var km: Double { return self * 1_000.0 }
var m: Double { return self }
var cm: Double { return self / 100.0 }
var mm: Double { return self / 1_000.0 }
var ft: Double { return self / 3.28084 }
}
使用扩展(Extension)可以扩展现有类型(struct,class ,enum,protocol)的内容,扩展支持计算属性、初始化器及方法。
8. 异常处理
调试时强行终止代码运行
-
使用 Xcode 的中断点 Breakpoint 功能
-
使用 fatalError() 函数
你可以使用
fatalError()去模拟一个严重错误,让程序在运行到这行代码时彻底停止运行。print()和fatalError()这类函数一般用于开发者调试时寻找错误,应在解决问题后移除这些代码。
应用中的异常处理
Swift 使用 Error 协议处理应用中的异常 。Swift 中的异常处理常被称作do-try-catch ,这是因为与异常处理相关是如下的一些关键词:
- 函数定义时应该明确标注其可能抛出 throw 错误
- 函数调用时需要先运行代码 do、尝试 try 可能抛出错误的函数并接住 catch 错误。
// Error
enum PasswordError: Error {
case notLongEnough
case tooLong
}
// Validate the length of a password
func validatePassword(_ password: String) throws -> Bool {
if password.count < 6 {
throw PasswordError.notLongEnough
} else if password.count > 20 {
throw PasswordError.tooLong
} else {
return true
}
}
var password = "1234678910"
// do-try-catch
do {
try validatePassword(password)
print("Validate Password")
} catch PasswordError.notLongEnough {
print("The password must be at least 6 digits.")
} catch PasswordError.tooLong {
print("The password must be no more than 20 digits.")
}
// try?
if let validateResult = try? validatePassword(password) {
print("Validate Result: \(validateResult), Validate Password.")
} else {
print("The password must be between 6-20 digits.")
}
// try!
try! validatePassword(password)